Accessible Canada Act: first federal accessibility legislation in Canada
- Solution
- Accessible Canada Act (ACA)
- Organization
- Canadian Department of Employment and Social Development
- Country of Implementation
- Canada
- Region
- North America
- Start Year
- 2019
- First published
- 16.01.2022

Solution details
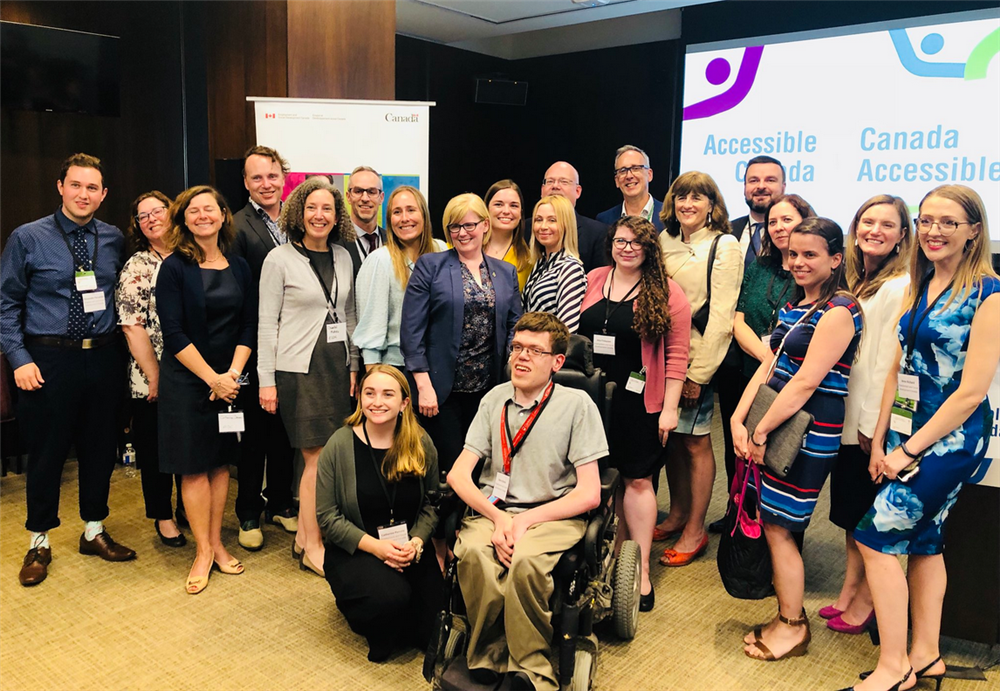
“ACA assures that all communities will welcome and celebrate the full participation of people with disabilities.” Bill Adair, Executive Director, Spinal Cord Injury Canada
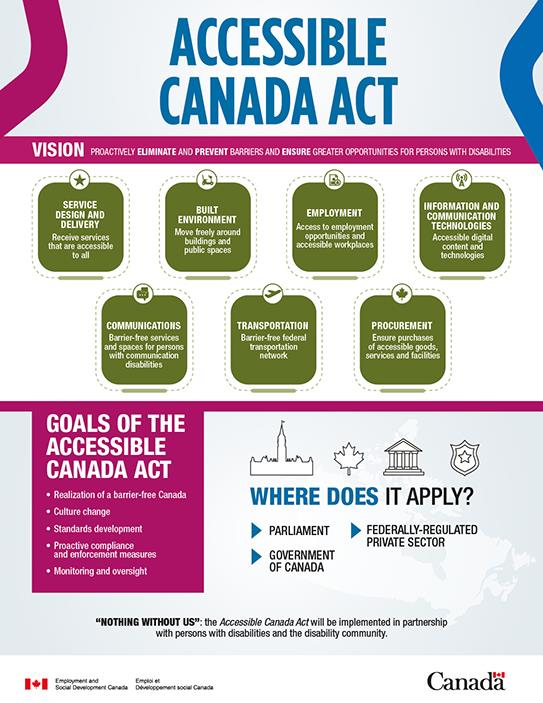
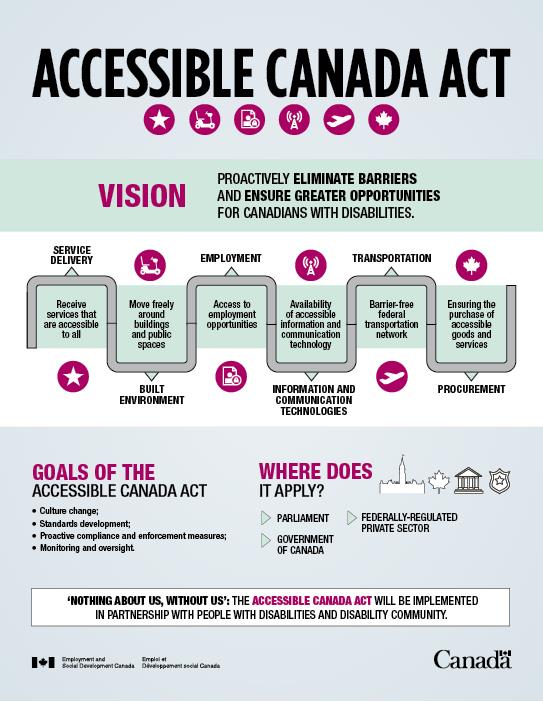
The ACA, passed by the Government of Canada in 2019, applies to all government departments and federally regulated agencies. It reflects input received through Canada's largest and most accessible consultation process. All legal entities are required to develop and publish multi-year accessibility plans and feedback mechanisms, enforced by the Accessibility Commissioner, who can also sanction with monetary penalties. A $229 million budget has been allocated to support the implementation.
Problems Targeted
Although 22 per cent of Canadians live with a disability, there was no national law to make and enforce accessibility standards and regulations in the country until 2019.
Solution, Innovation and Impact
The ACA is Canada’s first national law on accessibility, whose purpose is to make Canada barrier-free by 2040. It applies to all organizations under federal jurisdiction, including the Government of Canada and parts of the private sector that are federally regulated, such as banking, telecommunications, and transportation. Organizations are required to adhere to accessibility regulations and develop accessibility plans and feedback mechanisms. Enforcement differs depending on the organization or sector. The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission oversees compliance and enforcement for broadcasting and telecommunications services; the Canadian Transportation Agency oversees compliance and enforcement for the transportation sector. For all other organizations under federal jurisdiction there is an Accessibility Commissioner, who can issue penalties of up to $250,000 per violation. The law also establishes Accessibility Standards Canada, which develops standards in areas such as the built environment and employment. These standards can then become mandatory regulations.
Funding, Outlook and Transferability
$226 million have been allocated to the ACA over six years. Parliament will review the ACA five years after the first regulation is made, and the responsible minister will launch independent reviews of the Act every ten years. Accessibility requirements will be incorporated into all Government of Canada departments and agencies going forward.
Media
Related information
- Connections
- 2
-
Organization
- People